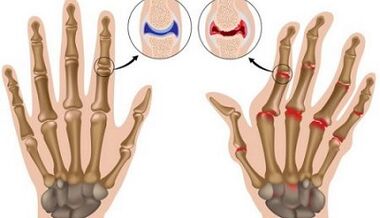
Joint diseases are one of the most common among skeletal pathology.Many suffer from arthrosis, various arthritis, not knowing the true nature of the disease and the causes that contribute to its development.Similar symptoms are misleading and interfering with understanding what is actually happening with the joints and what is the difference between these diseases.
Arthritis is a disease of inflammatory origin, characterized by damage to the synovial capsule.In the mechanism of development of various types of the disease, there are infectious, immune, metabolic, allergic factors.Arthrosis is characterized by degenerative-dystrophic processes in all tissues of the joint (cartilage, synovial shell, subchondral bone, ligaments, muscles).
It must be remembered that in doubtful cases, only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment.
Reasons
There are various adverse factors that can provoke inflammation or dystrophy in the joints.Their accounting helps to find out the risk of arthrosis or arthritis in the patient, and the elimination of etiological moments will make it possible to cure the disease in the early stages.
The etiology of arthritis
The disease can develop at any age and with many pathological processes in the body, so it is important to clearly understand which factors need to be affected.
Inflammation of the joints can be primary, observed with such pathologies:
- Rheumatoid and juvenile arthritis.
- Gout.
- Bekhterev disease.
In addition, there are a number of diseases against which the joints are affected secondly:
- System red lupus.
- Psoriasis.
- Hemorrhagic diathesis and vasculitis.
- Jersiniosis, salmonellosis, gonorrhea, chlamydia.
- Hepatitis.
- Sepsis and others.
Etiology of arthrosis
Unlike arthritis, deforming arthrosis is an independent disease, but its development can still be triggered by frequent inflammation of the joints in a history of the joint.
The main risk factors for osteoarthritis will be:
- Elderly age.
- Estrogen deficiency in women.
- Overweight.
- Injuries and joint operations, overload.
- Heredity.
The clarification of the causes of the disease already during the patient survey will begin to start a differential diagnosis to determine how arthrosis is different.
Symptoms
With various arthritis with arthrosis, patients are primarily concerned about joint pain, which in certain situations may intensify.The swelling and limitation of movements in the affected skeletal areas is noted, one can notice the deformation of the joints.
With arthritis or arthrosis, both individual joints and entire groups can be affected, up to the development of a generalized process.
Clinical symptoms in articular diseases have much in common.However, you should carefully evaluate the characteristic differences of arthritis and deforming arthrosis.
Arthritis clinic
Inflammation of the joint capsule is accompanied by local and common symptoms.Local symptoms are caused by a sprain of the synovial membrane with an accumulated exudate.The pains will be sharp, moderate or strong, which bother almost constantly, intensifying during movements, and sometimes at night.In certain situations, they can be migrating.
The redness and increase of the skin temperature over the joint, expressed swelling of the tissues is also noted.
For rheumatoid arthritis, prolonged morning stiffness, as well as characteristic deformations (“Swan’s neck”, “Butonerka”) will be constant.If there is an infectious pathology, then the general condition of the patient also suffers - there is a fever, weakness, and malaise.Especially important is the presence of characteristic signs of a general disease, which caused the joint inflammation.
Clinic of osteoarthrosis
Since inflammation is given a lower role in arthrosis than arthritis, local signs will not be so pronounced.Pain arise at the beginning of movements, intensifying at a long load, and in the future - at rest.Crown and friction in the joints are characteristic.Short -term stiffness is also possible.
Patients experience significant difficulties in movements in the affected limbs.
The difference between deforming arthrosis and arthritis is that the disease has a long course, but slowly and steadily progresses, leading to disability.
Additional methods
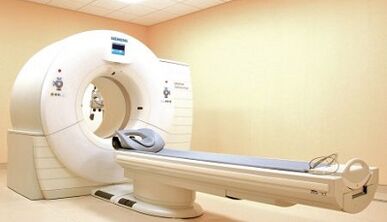
The difference between arthritis and arthrosis helps to establish additional diagnostic methods.You can differentiate these conditions using laboratory and instrumental methods that have their advantages in different situations.
Diagnostics of arthritis and deforming arthrosis are engaged in arthrologists and traumatologists with the involvement of related specialists.
You can confirm the articular defeat using:
- Radiography.
- Computer and magnetic resonance imaging.
- Arthroscopy.
Diagnosis of arthritis
Laboratory tests are of particular importance in determining the causes of the disease.They allow you to determine the type of microbial agent, impaired immune status and biochemical processes.The results of the analysis of the exudate will indicate the nature of the inflammatory process.
During the instrumental examination, you can notice characteristic changes in the joints:
- Erosion and bone ankyloses - with rheumatoid inflammation.
- “Symptom of the Punch” - with gout.
- Uzura, osteosclerosis in sacral and illegal joints-in the illness of Bekhterev.
Diagnosis of osteoarthritis
Unlike arthritis, with arthrosis, laboratory tests are not important.The results of radiological methods are the forefront, which allow you to identify the characteristic features of osteoarthrosis:
- The narrowing of the joint gap.
- Periosword osteoporosis.
- The formation of osteophytes.
Diagnosis of arthritis and deforming arthrosis using additional methods makes it possible to accurately establish the type of disease for its timely treatment.
Therapy
Arthritis from arthrosis also distinguish the methods of therapeutic effect on the pathological process.You can treat diseases not only with traditional methods and drugs, but in some cases folk remedies, using them at home.Therapy should be complex: etiotropic, pathogenetic and symptomatic.
And also include the use of drugs in various forms: injections, tablets, ointments.
For the treatment of deforming arthrosis and arthrites, such medications can be used:
- Anti -inflammatory drugs.
- Analgesics.
- Drugs that improve blood circulation.
- Vitamins.
The use of drugs should be justified: for each patient the optimal doses and the course of administration are prescribed, and folk methods are used only in agreement with the attending physician.
Treatment of arthritis
With the secondary nature of the process, it is necessary to treat the underlying disease, which distinguishes arthritis from arthrosis.First, injections of drugs are injected, and after the elimination of exacerbation, you can switch to taking drugs in tablets:
- An important place in the treatment of inflammation is given to antibiotics, especially for sepsis.If the damage to the joints is caused by systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis, it is necessary to use cytostatics and hormones, with gout - uricosuric drugs, and in the case of hemorrhagic diathesis - hemostatic drugs.With psoriasis, a special place is given to medicines in ointments.
- If the cause of the articular pathology was the illness of Bekhterev or gout, during the period of remission you can also use physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises, the exercises of which are also shown at home.
- In the treatment of acute purulent inflammation, it is necessary to conduct a joint puncture for the evacuation of exudate, followed by washing with antibiotics and taking drugs.
Treatment of osteoarthritis
Unlike arthritis, with arthrosis, the additional use of chondroprotectors (in tablets or injections), as well as calcium and vitamin D.
The possibilities of physiotherapy are also widely used:
- Electrophoresis of drugs.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Laser treatment.
- Paraffin and mud.
- Balneotherapy.
Be sure to include exercises of therapeutic gymnastics, massage in a complex of therapy.You can treat osteoarthritis with folk remedies, using recipes for non -traditional medicine at home:
- Reception of gelatin.
- Infusions from St. John's wort, juniper, birch buds.
- Compresses with honey and oatmeal.
- Ointment from hops, Donnik and St. John's wort.
Folk methods can be used at home in parallel with pills prescribed by a doctor and anti -inflammatory ointments, but not instead of them.
Prevention
The prevention of arthrosis and arthritis also has its differences.To prevent osteoarthrosis, you need to fight overweight, avoid joint injuries, normalize hormonal background in postmenopausa.
When inflammation of the joints, it is important to prevent infectious diseases and treat them in time.
In many cases, various dietary recommendations must be observed.
In order to say how arthritis differs from arthrosis, you need to pay attention to all these points.These diseases have not only similar features, but also fundamental differences that everyone should know.